Table of Contents Show
Sneezing is a natural and healthy reflex that helps us clear our nasal passages and protect ourselves from infections. But sometimes, sneezing can also cause a sharp and agonizing pain in your arms that makes you wonder if something is seriously wrong with your body. What causes this pain and how can you prevent it from happening?


In this article, we will explore the possible causes, treatments, and prevention tips for pain in arms after sneezing. We will also answer some of the most frequently asked questions about this condition. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of why your arms hurt when you sneeze and what you can do about it.
What Causes pain in arms after sneezing?


There are several possible causes of pain in arms after sneezing, ranging from minor to serious. Some of the most common ones are:
Muscle strain:
When you sneeze, your chest muscles contract forcefully and quickly, which can put a strain on your arm muscles as well. This can cause a temporary pain or soreness in your arms, especially if you have been holding something tight or lifting something heavy before sneezing. The pain usually goes away on its own after a few minutes or hours.
Pinched nerve:
A pinched nerve occurs when a nerve is compressed or irritated by surrounding tissues, such as bones, muscles, or discs. This can cause pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected area. A pinched nerve in your neck or upper back can affect the nerves that run down your arms and cause pain when you sneeze. The pain may radiate from your neck to your shoulder, elbow, wrist, or fingers.
Spinal disc herniation:
A spinal disc herniation occurs when a disc between two vertebrae bulges out and presses on a nerve root. This can cause severe pain in your back and arms, as well as numbness, tingling, or weakness. A disc herniation in your cervical spine (neck) can affect the nerves that control your arms and cause pain when you sneeze. The pain may be worse when you bend your neck forward or backward.
Spinal stenosis:
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal, which is the space where the spinal cord and nerves pass through. This can cause pressure on the spinal cord and nerves and lead to pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in various parts of the body. Spinal stenosis in your cervical spine (neck) can affect the nerves that control your arms and cause pain when you sneeze. The pain may be worse when you extend your neck or look up.
Costochondritis:
Costochondritis is an inflammation of the cartilage that connects your ribs to your breastbone (sternum). This can cause chest pain that may radiate to your arms, especially when you cough or sneeze. The pain may be sharp, stabbing, or burning and may worsen when you breathe deeply or move your upper body.
Heart attack:
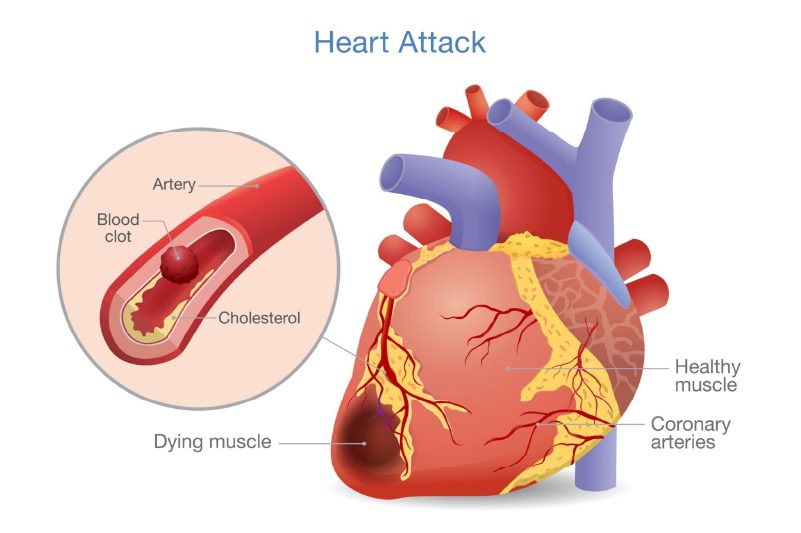

A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to a part of your heart muscle is blocked by a clot or plaque. This can cause chest pain that may spread to your arms, neck, jaw, or back. The pain may be severe, crushing, squeezing, or pressure-like and may last for more than a few minutes. You may also experience shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, sweating, dizziness, or fainting. A heart attack is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention.
How to diagnose the cause of pain in arms after sneezing

If you experience pain in arms after sneezing, you should consult your doctor to find out the underlying cause and get proper treatment. The diagnosis of arm pain after sneezing depends on several factors, such as the location, duration, intensity, and frequency of the pain, as well as any other symptoms or medical conditions you may have. Your doctor will use various methods to diagnose the cause of your arm pain after sneezing, such as:
- Medical history: Your doctor will ask you questions about your medical history, such as when did the pain start, how often does it occur, what triggers it, what relieves it, and whether you have any other health problems or risk factors. Your doctor will also ask you about your lifestyle habits, such as smoking, drinking, exercise, and medication use. This will help your doctor to rule out or confirm some possible causes of arm pain after sneezing, such as muscle strain, nerve compression, joint inflammation, heart attack, aortic dissection, pulmonary embolism, etc.
- Physical examination: Your doctor will examine your arm and check for any signs of injury, infection, inflammation, or nerve damage. Your doctor will also check your blood pressure, pulse, temperature, and respiratory rate. Your doctor may also perform some tests to assess the function and sensation of your arm, such as tapping your elbow or wrist to elicit a reflex response or asking you to move your fingers or shoulder. This will help your doctor to determine the location and severity of the problem and to identify any possible complications.
- Imaging tests: Your doctor may order some imaging tests to get a clearer picture of the structure and function of your arm and other organs. These tests may include X-rays, ultrasound, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), CT (computed tomography) scan, or angiography. These tests can help your doctor to detect any abnormalities in your bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, blood vessels, or organs that may cause arm pain after sneezing. For example, an X-ray can show a fracture or dislocation of the arm; an ultrasound can show a blood clot or aneurysm in the arm; an MRI can show a herniated disc or spinal cord compression in the neck; a CT scan can show a lung infection or tumor; and an angiography can show a blockage or rupture of an artery in the chest or arm.
- Other tests: Depending on the suspected cause of pain in arms after sneezing, your doctor may also order some other tests to confirm the diagnosis and to monitor your condition. These tests may include blood tests, urine tests, electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram (ECHO), pulmonary function tests (PFTs), or nerve conduction studies (NCS). These tests can help your doctor to measure the levels of certain substances in your body that may indicate infection, inflammation, or damage; to evaluate the electrical activity and function of your heart; to assess the capacity and function of your lungs; or to measure the speed and strength of the signals transmitted by your nerves.
The diagnosis of pain in arms after sneezing is important to determine the appropriate treatment and to prevent any serious complications. Therefore, if you have arm pain after sneezing that persists or worsens over time, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible.
How to Treat pain in arms after sneezing?
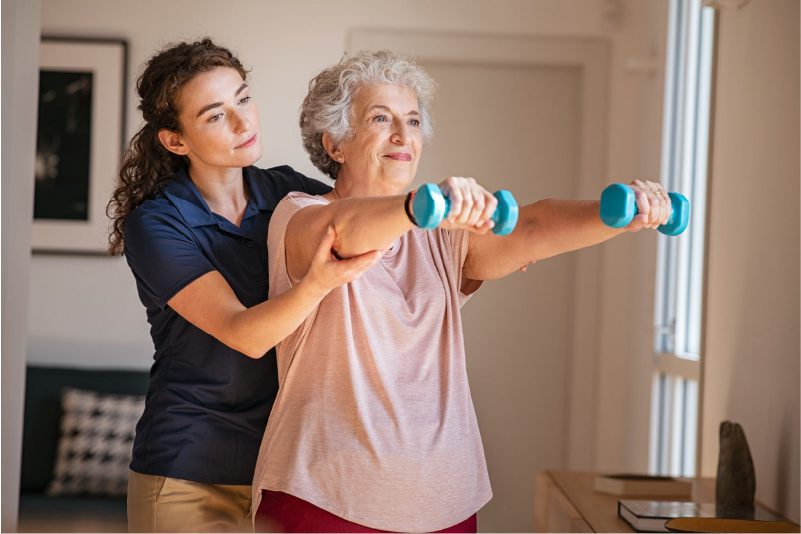


The treatment for pain in arms after sneezing depends on the underlying cause and severity of the pain. Some general tips are:
- Rest: If the pain is mild and caused by muscle strain or pinched nerve, you may benefit from resting your arms and avoiding any activities that worsen the pain. You may also apply heat or ice packs to the affected area to reduce inflammation and ease discomfort.
- Medication: If the pain is moderate to severe and caused by spinal disc herniation, spinal stenosis, costochondritis, or heart attack, you may need to take medication to relieve the pain and treat the underlying condition. Depending on the cause, you may be prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, nerve pain medications, or blood thinners. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and do not take more than the recommended dose.
- Physical therapy: If the pain is chronic and caused by spinal disc herniation, spinal stenosis, or pinched nerve, you may benefit from physical therapy to strengthen your muscles and improve your posture and flexibility. A physical therapist can teach you exercises and stretches that can help reduce pressure on your nerves and discs and prevent further injury.
- Surgery: If the pain is severe and does not respond to conservative treatments, or if the cause is life-threatening, such as a heart attack, you may need surgery to correct the problem. Depending on the cause, you may undergo a spinal decompression surgery, a spinal fusion surgery, a disc replacement surgery, or a coronary artery bypass surgery. Surgery is usually the last resort and involves certain risks and complications.
How to Prevent pain in arms after sneezing?
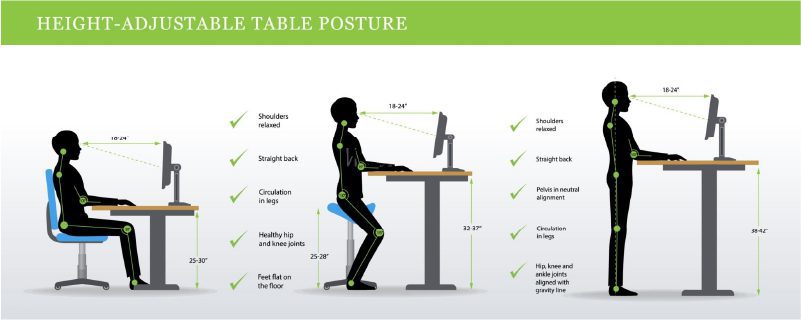

The best way to prevent pain in arms after sneezing is to prevent or manage the underlying condition that causes it. Some preventive measures are:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can put extra stress on your spine and joints and increase your risk of developing spinal disc herniation, spinal stenosis, or heart disease. Try to maintain a healthy weight by eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking can damage your blood vessels and increase your risk of developing plaque or clots that can block the blood flow to your heart or brain. Smoking can also worsen your cough and sneeze reflex and increase your risk of developing costochondritis. Quit smoking or seek help from your doctor if you need assistance.
- Practice good posture: Poor posture can strain your muscles and ligaments and cause your spine to become misaligned. This can lead to pinched nerves, disc herniation, or spinal stenosis. Practice good posture by keeping your head, neck, and back in a straight line and avoiding slouching or hunching. You may also use ergonomic furniture and devices that can support your spine and reduce tension.
- Limit alcohol intake: Drinking too much alcohol can raise your blood pressure and cholesterol levels and increase your risk of developing heart disease or stroke. Alcohol can also irritate your throat and nasal passages and trigger sneezing. Limit your alcohol intake to no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Manage stress: Stress can cause muscle tension and inflammation and affect your immune system and blood pressure. Stress can also make you more prone to sneezing due to allergies or infections. Manage stress by practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or massage. You may also seek counseling or therapy if you need professional help.
When to see a doctor for pain in arms after sneezing
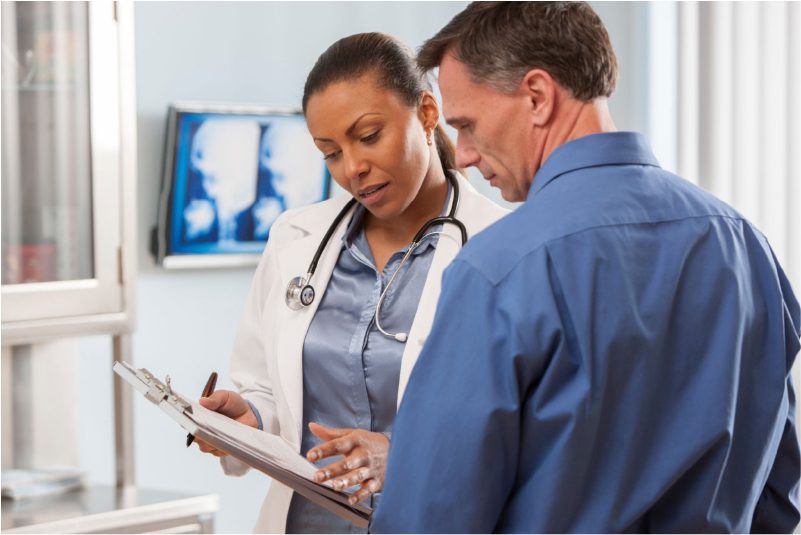


Pain in arms after sneezing is usually not a serious condition and can be treated with home remedies or over-the-counter medications. However, in some cases, it may indicate an underlying problem that requires medical attention. You should see a doctor for arm pain after sneezing if you experience any of the following:
- Severity: The pain is severe, sharp, or stabbing and does not improve with rest, ice, or painkillers. This could indicate a muscle tear, a nerve injury, or a heart attack.
- Duration: The pain lasts for more than a few minutes or hours and does not go away with time. This could indicate a chronic condition such as arthritis, tendinitis, or carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Frequency: The pain occurs frequently or every time you sneeze. This could indicate a structural problem such as a herniated disc, a spinal stenosis, or a bone spur.
- Associated symptoms: The pain is accompanied by other symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness, swelling, redness, fever, chest pain, shortness of breath, coughing up blood, or weight loss. These could indicate a serious condition such as a stroke, an infection, a tumor, or a lung disease.
If you have any of these signs or symptoms, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. Your doctor will ask you about your medical history, perform a physical examination, and order some tests to determine the cause of your arm pain after sneezing. Depending on the diagnosis, your doctor will prescribe the appropriate treatment for your condition.
FAQs About pain in arms after sneezing
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about pain in arms after sneezing:
Q: Is pain in arms after sneezing a sign of a heart attack?
A: pain in arms after sneezing can be a sign of a heart attack, but it is not the only possible cause. Other causes of pain in arms after sneezing include muscle strain, pinched nerve, spinal disc herniation, spinal stenosis, costochondritis, etc. If you experience pain in arms after sneezing along with other symptoms of a heart attack, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, sweating, dizziness, or fainting, you should call 911 immediately.
Q: How long does pain in arms after sneezing last?
A: The duration of pain in arms after sneezing depends on the cause and severity of the pain. In most cases, the pain lasts for only a few seconds or minutes and goes away on its own. However, in some cases, the pain may last for hours or days and require medical attention.
Q: Can I prevent pain in arms after sneezing by holding my nose?
A: Holding your nose when you sneeze can prevent air from escaping through your nostrils, but it can also increase the pressure in your chest cavity and sinuses. This can worsen the pain in your arms or cause other complications, such as ear infection, nosebleed, or ruptured eardrum. It is better to let the sneeze out naturally and cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow.
Q: What are some home remedies for pain in arms after sneezing?
A: Some home remedies for pain in arms after sneezing are:
- Apply heat or ice packs to the affected area to reduce inflammation and ease discomfort.
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, to relieve mild to moderate pain.
- Massage or stretch your arms gently to relax your muscles and improve blood circulation.
- Drink plenty of water and fluids to stay hydrated and thin out any mucus that may trigger sneezing.
- Use saline nasal spray or neti pot to rinse out any irritants from your nasal passages that may cause sneezing.
Conclusion on Pain in Arms After Sneezing
Pain in arms after sneezing is a common phenomenon that many people experience at some point in their lives. It can be caused by various factors, such as muscle strain, nerve compression, spine dislocation, or underlying medical conditions. The pain usually lasts for a few seconds or minutes, but it can be very uncomfortable and alarming for some people.
The most likely cause of pain in arms after sneezing is muscle strain or tension. When we sneeze, we contract our chest, abdominal, and upper back muscles with great force and speed. This sudden movement can put stress on the muscles and tendons that connect the arms to the shoulders and neck. If these muscles are already tight or weak, they can become inflamed or injured by the sneeze. This can result in pain, stiffness, or tingling in the arms or shoulders.
Another possible cause of pain in arms after sneezing is nerve compression or pinching. The nerves that supply sensation and movement to the arms originate from the spinal cord in the neck and upper back. These nerves can be compressed or irritated by various factors, such as poor posture, spinal disc problems, arthritis, or injuries. When we sneeze, we increase the pressure inside our chest and spine. This can aggravate the nerve compression and cause pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms.
A less common but more serious cause of pain in arms after sneezing is spine dislocation or subluxation. This is a condition where one or more of the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine) move out of their normal position and affect the surrounding tissues and nerves. This can happen due to trauma, degeneration, or congenital defects. Spine dislocation can cause severe pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the neck and back. It can also affect the nerves that control the arms and cause pain, tingling, or paralysis.
Some underlying medical conditions can also cause pain in arms after sneezing. These include fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, multiple sclerosis, and stroke. These conditions can affect the nervous system and cause widespread pain and sensitivity to stimuli. Sneezing can trigger or worsen the pain in these cases.
The treatment for pain in arms after sneezing depends on the cause and severity of the pain. In most cases, the pain is mild and temporary and does not require any specific treatment. However, some home remedies can help relieve the discomfort, such as applying ice or heat to the affected area, taking over-the-counter painkillers, stretching or massaging the muscles, and improving posture and ergonomics. If the pain is persistent or severe, it is advisable to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. The doctor may prescribe medication, physical therapy, chiropractic care, surgery, or other interventions depending on the cause of the pain.
In conclusion, pain in arms after sneezing is not a rare or dangerous condition in most cases. It is usually caused by muscle strain or nerve compression due to the sudden and forceful movement of sneezing. However, it can also be a sign of more serious problems such as spine dislocation or underlying medical conditions. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the frequency and intensity of the pain and seek medical help if necessary.
I hope you found this article helpful and informative. If you have any questions or feedback, please feel free to leave a comment below. Thank you for reading!





Comments 3
Comments are closed.